What is ElectroPolishing?
Electropolishing or also known as electrochemical polishing, anodic polishing, and electrolytic polishing is really useful for polishing and deburring parts that have complex geometries or are fragile. Electropolishing is an electrochemical finishing process that removes a thin layer of material from a metal part, typically stainless steel or identical alloys. The Electropolishing process leaves a smooth, shiny, and ultraclean surface finish.
The Electropolishing process is different from passivation, However, it is still easy to confuse the two processes. Both are non-mechanical, chemical processes, but only electropolishing uses electrical current. Both processes are intended to improve corrosion resistance.
How Does Electropolishing Work?
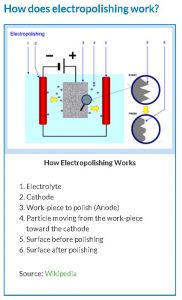
In electropolishing, the metal part serves as the positively charged anode. The workpiece is connected to the positive terminal of a DC power rectifier and the negatively charged anode, generally made of stainless steel or zirconium is connected to the negative terminal of the DC power rectifier.
Both Anode and cathode are immersed in a temperature controller bath of electrolyte solution, typically consisting of a high viscosity mixture of sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid. Electrical current from the rectifier is conducted from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte. The electrical current causes metal ions on the surface of the part to oxidize and dissolve into the electrolyte. The process can dissolve extremely small, tightly controlled amounts of metal, resulting in a micron-level thickness of surface removal.
The amount of metal surface removal is controlled by the following factors :
- Electrolyte chemical composition
- The temperature of electrolyte (typically 170°F – 180 °F)
- Length of time exposure to electrical current
- The density of electrical current (varies by an electrolyte; the typical range is 140 – 250 amps per square foot)
- Composition of metal alloy undergoing electropolishing.
The preferential removal of rotuding portions of the surface structure leads to a smoother metal surface.
Who Use Electropolishing?
In the past since the 1950s, scientists have commercially used the combination of chemicals and electricity to improve the surface finish of metals. Below is a wide variety of industries that use electropolishing :
- Surgeons and dentists use electropolishing to keep their tools clean and functioning well.
- Food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processors benefit from the sterilizing features of electropolishing.
- Appliance manufacturers use electropolishing in appliances like refrigerators and washing machines to make parts last longer and look better.
- Aerospace manufacturers use electropolishing on flight-critical parts to reduce friction and ensure top performance.
- Semiconductor manufacturers use electropolishing with fragile, irregularly-shaped products.
- Automakers and the racing industry electropolish gears and fuel lines to reduce friction, boost performance and ensure the long life of parts.
Examples of metal parts that are commonly electropolished: Piping and tubing, Fasteners, Springs, Wire racks, Blades, etc.
Electropolishing Stainless Steel
Electropolishing of stainless steel is the most common use of the process. Even though almost any metal will work, the most often electropolished metals are 300- and 400- series stainless steel. Also, other metals that are compatible with electropolishing are Alumunium, Brass, Carbon Steels, Cobalt Chrome, Nickel Alloys, Titanium, Nitinol.
Also note that only limited success with cast metals, like alloys containing significant amounts of silicon, sulfur, or carbon. Electropolishing aluminum and zinc die casting does not work well, but almost all other aluminum yield good results, Titanium, and nitinol are also compatible with electropolishing; however, the electrolyte solution for these metals is highly flammable and requires chiller so the electrolyte won’t combusting at room temperature.
Advantage Of Using Investment Casting
- Flexible Design
- Less Waste, Strong Manufacturing Cost
- Tighter Tolerance (More Precise)
- Excellent and smooth surface finish
- Reduce the need for secondary machining.
- Wide selection of cast metals and alloys
Why Should You Choose Zenith?
- Engineering, With 20 years of experience in Lostwax Casting, we are experts in casting any kind of products and materials. Updating knowledge is a must as part of our Engineering team’s daily workload.
- Quality Focus, Our focus is Zero defects at the customer site.With ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485:2016, CE Marking and PED 2014/68/EU Annex. I,4.3 & AD 2000-W0 certified, we have a system to control every production step to get the required quality that customer needs,
- High Capacity, Our capacity a month can cover 120 tons with available induction furnaces range from 100kg, 150kg, and 250 kg.We also have 1 dedicated line for medical products (zenmed+)
- IT Utilize System, With every process is managed using a cloud system, the information flow is very quick and accessible everywhere & anytime.We also enable Extranet for customers to check their PO progress and related information and documents.
- Lean Manufacturing, By applying Lean Manufacturing, every process steps is Visual Controlled and Every Waste is identified and controlled using Continuous Improvement/Kaizen.
- Health, Safety, & CRS, By having certified for ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 14001:2015, We are committed to concern with our People Health, Safety & Environment. We are also a permanent donator for Indonesia Cancer Foundation and supporting Orphans nearby the Factory.
Contact Us

Mill Test Certificate EN 10204
What is Mill Test Certificate? Mill Test Certificate, is a provided by a manufacturer to certify the chemical composition and mechanical composition of the product, this thing is really important in this industry especially with products related in medical like...

CAD/CAM? – Beginner Guide About Machining
CAD and CAM? What is that? CAD/CAM also called computer-aided design & computer-aided manufacturing is software used to design and manufacture products and their prototype, this software usually related to CNC machines. How does it work? In addition to the...

What is Drilling? A Beginner’s Guide About Machining.
What is Drilling? Drilling is a cutting process using a drill bit to create holes in the workplace, this process is the one most common method used in the machining process. Here's in CNC drilling have many scopes, starts from simple into the complex one. CNC Drilling...

What is Machining Process? A Beginner’s Guide About Machining
Machining? Machining is a process in which a controlled material removal machine is used to remove some parts from the workpiece to shape it into the intended design. This process is a part of the manufacturing of many products based on metals, however it's possible...

The Difference Between Investment Casting and Sand Casting
Investment Casting and Sand Casting In this post, we will learn the difference between investment casting and sand casting, these two were the most popular method used in metalworking industry. Image 1.1 Investment and sand casting product What Is Casting? In the...