Gating System of Investment Casting
Our first article made investment casting seems so simple, as if you only need to make wax pattern, make mold, melt metal, and pour the metal into the mold. Unfortunately, the actual metallurgy practice is more complicated than that. This article helps understanding: How to design gating system for precision casting?
First, let’s discuss about investment casting mold. The functions of the mold are the delivery of metal liquid and the shaping of final product. The mold is only used once and is disposable after the casting. Look into our previous article to refresh about precision casting process, especially mold production which result in negative cavity for metal filling. As already mentioned in the previous article, the cavity forms after the lost-wax process. Before filling the cavity, liquid metal passes through gating system to optimize metal delivery and improve the product casting quality.
Gating System
Liquid metal adapts to the shape of mold cavity. This is the reason metal casting has been popularly used. Product shaping is possible regardless of shape complexity as long as liquid metal can properly fill the mold. Nonetheless,the design of the mold requires more than the shape of the product.
Proper mold design makes cutbacks in problems associated with investment casting. During the mold design, you need to draw more than just the products, but also their gating system (metal delivery system) to result in high quality products. Gating system guides and delivers the liquid metal flow from the mold entrance (pouring cup) to the product cavity. The purpose of gating system is to achieve better product quality by reducing casting defects, for example: shrinkage, incomplete filling, etc.

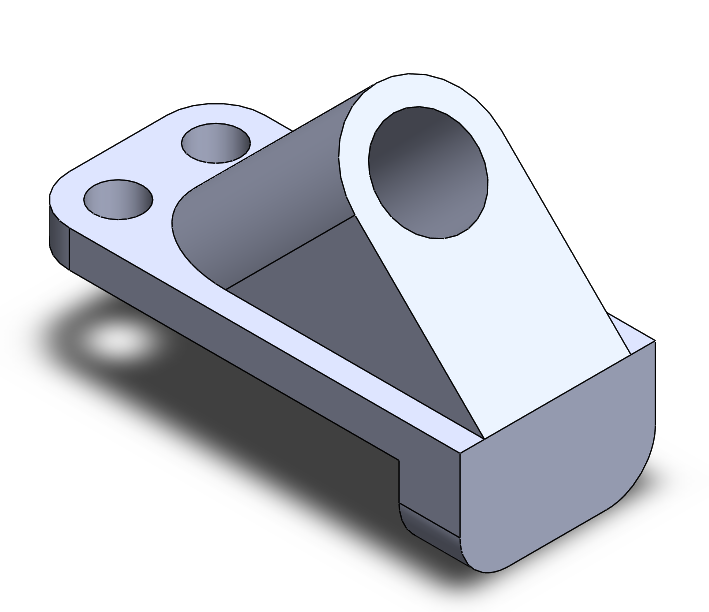
Picture 1 Gating System Design consist of Pouring Cup+Wax Trunk, Cup Crown, and Sticks. They will later be assembled to form pattern gating system.
Gating System Design
Gating system design ensures proper metal delivery and controls the delivery rate. As such, gating system design governs the fluid flow and consequently prevents insufficient metal feeding, turbulence, and premature solidification. In this article, we will discuss components in gating system: pouring cup, feeder, runner, and ingates.
The heat transfer rate of liquid metal controls the solidification time and cooling rate. Gating system design can adjust the volume-to-surface ratio to engineer solidification time and cooling rate. If the volume-to-surface ratio increases, there are less surface area for heat transfer, and heat conducts slower. So, this adds more solidification time and vice versa. It is worth noting that the metal solidification rate may not be uniform all over the mold.
In industrial practice, gating systems are assembled from wax pattern cup, wax pattern trunk, and so on. Both product pattern and gating system pattern use the same wax material. Both of them vaporize during lost-wax process (de-waxing). Take a look at Picture 2 to compare between a product (left) and products assembled in gating system (middle, right).


Picture 2 (Left) A product example, (Middle) Top view of products assembled onto wax pattern tree, (Right) Bottom view of products assembled onto wax pattern tree.

Picture 3 Pouring Cup, Feeder, and Feeder extension.
Pouring cup design
Pouring cup (observed in Picture 3) collects pouring liquid metal and facilitates metal flow into the mold. It is the liquid metal entrance into mold cavity. In investment casting, it also acts as reservoir to supply extra metal if required.
Proper gating system design can also trap slags, dross, and inclusions from entering the product cavity. Light inclusions float to pouring cup given enough time due to lower density compared to liquid metal. They may present in the melt or/and form during pouring. Re-oxidation is the most frequent origin of inclusions. Some inclusions can also originate from the melting and casting equipment, even from the mold debris.
Feeder design
Feeder (observed in Picture 3) in investment casting serves the function of sand casting’s sprue and riser. In investment casting, wax trunk forms this feeder path. Casting design usually spares extra metal-feed volume to anticipate shrinkage during cooling (reservoir metal). During solidification and cooling, metal contracts as temperature decrease, then the reservoir metal from feeder can squeeze into the shrinkage area.This extra metal cools later, so it can fill the section where metal shrink. Depending on the shape complexity, engineers may also add extra feeders.
The presence of feeder also improves the quality of casting. Sufficient length allows metal and inclusions to separate themselves based on density, so the lighter inclusions floats without entering the casting cavity. Engineers usually locate feeders in complicated part of the product, for example close to the corner of the product. Another benefit of a feeder is to also provide spaces to trap shrinkage voids, gasses and dross. Engineers should design carefully so when feeder acts as metal reservoir, it comes from cleaner part of the feeder.
The height of the feeder is related to the velocity of the flow, which will determine the metal feeding rate. If the flow is too fast, the fluid flow can cause turbulence that can consequently cause gas entrapment. In some metals, gases form bubbles or/and stimulates oxide formation inside the mold.
During the practice of liquid metal pouring, the first metal liquid that enters the gating system and mold are more susceptible to oxidation (in the air) and inclusions (from molds, etc). As such, engineers can set feeder extension to trap these relatively dirty metal liquid. This feeder extension can also be seen from Picture 3.
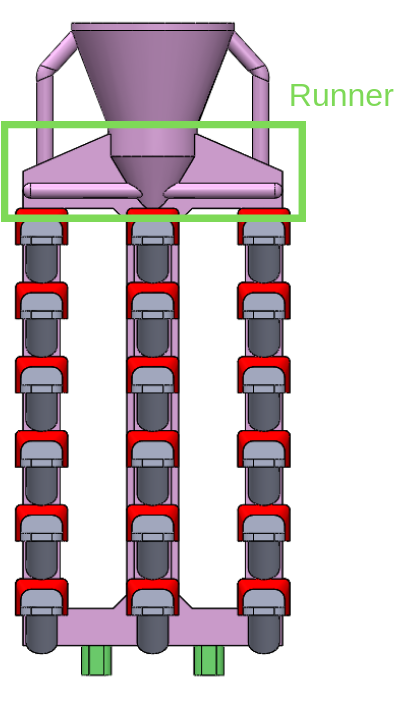
Picture 4 Runner
Runner design
Runner (observed in Picture 4) distributes liquid metal to optimize metal supply mechanism. It guides liquid flow to fill targeted product cavity. Also, it allows multiple metal delivery channel, which enables a mold to hold multiple product cavities. This adds economical value to foundry practice. Adding more parallel runners can also help facilitating better metal filling in complex or heavy parts. Size of the runner also influences feeding rate into ingates, which later relates to the feeding rate into product cavity.
Ingates design
Ingate (observed in Picture 5) is the last gating system component right before the casting product, connecting runners and products. Engineers usually connect ingates onto the thicker part of the metal to prevent metal solidify early and block the pathway. In some of these cases, engineers use mutiple ingates onto the same product to anticipate if any of the ingates become hot spot. Please note that adding more parallel ingates slows feeding rate into the product cavity. To tackle this issue, engineers can reduce the size of ingates, thus increasing feeding rate.
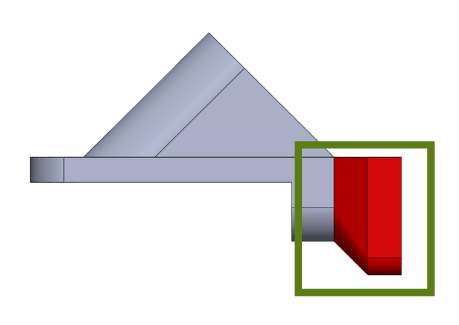
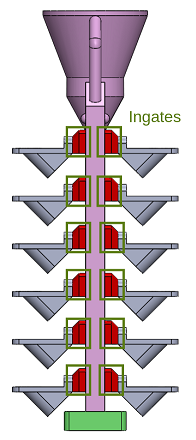
Picture 5 (Left) Ingate connects to the product (Right) Ingates connect products and gating system.
Efficient Gating System Design
The economical aspect is as important as the engineering aspect, so gating system design needs to be cost efficient. The most straightforward indicator is the yield ratio, which is the weight ratio of the product in comparison to the total cast (product+gating system). Good gating system design performs at high yield ratio without compromising the gating system function. Foundry practice returns and recyles the leftover gating system to supply the following casting batch.
In addition, engineers also consider the subsequent processing stages, such as cutting, blasting, as so on. Practically, it should be easy to remove gating system and product. Otherwise, the cutting stage will be costly. Experienced engineers estimate gating system design cost as the final product production cost, not just product casting cost.
Gating system design in Zenith Allmart Precisindo?
Zenith Allmart Precisindo employs a team of experts with 20 years of experience in precision casting/lost-wax casting industry. We have cast a wide variety of products, from a small medical implant to a large impeller and we can definitely design the gating system of your products. Please check our portfolio here to learn more about our company products!
Zenith Allmart Precisindo is more than merely your metal casting supplier or vendor. We want to grow together with you, and we will solve your manufacturing challenges using our advanced technology, professional practice, and manufacturing knowledge. Contact us here for more information!

What Is Tooling In Investment Castings?
Tooling in Investment Casting is considered to be wax-injection dies that are used to create wax patterns. If you're following us from our previous trivia posts or you're familiar with how investment casting works, you already know that these wax patterns form the...

Preparing Shell for Lost Wax Casting
Description The Investment Casting Process is to coat multiple layers of refractory coatings on the surface of the wax mold. Afterward, it is dried and hardened, the wax mold is melted by heating to obtain a shell with a cavity that matches the shape of the wax...

What is ElectroPolishing?
Electropolishing or also known as electrochemical polishing, anodic polishing, and electrolytic polishing is really useful for polishing and deburring parts that have complex geometries or are fragile. Electropolishing is an electrochemical finishing process that...

What Is Cast Steel Pouring Process?
Description In investment casting, the process of pouring cast steel is a very important step. The most commonly used pouring method in investment casting is gravity pouring. First, the molten steel is poured from the furnace into the casting ladle and then...

Mold Material Defects
Mold Materials Defects In investment casting, defects are a common problem, for example, this can't be happening in the medical industry, because of its high standard so the finished product needs to be as precise as possible. Mold material defects usually caused by...

What is Casting Defects? Gas Porosity and Shrinkage
What is Casting Defects? Casting defects happen when undesired irregularity happens in the metal casting process, there is many types of defects in the metal casting industry as such: Gas porosity Shrinkage Mould material defects Pouring metal defects Metallurgical...

Mill Test Certificate EN 10204
What is Mill Test Certificate? Mill Test Certificate, is a provided by a manufacturer to certify the chemical composition and mechanical composition of the product, this thing is really important in this industry especially with products related in medical like...

CAD/CAM? – Beginner Guide About Machining
CAD and CAM? What is that? CAD/CAM also called computer-aided design & computer-aided manufacturing is software used to design and manufacture products and their prototype, this software usually related to CNC machines. How does it work? In addition to the...

What is Drilling? A Beginner’s Guide About Machining.
What is Drilling? Drilling is a cutting process using a drill bit to create holes in the workplace, this process is the one most common method used in the machining process. Here's in CNC drilling have many scopes, starts from simple into the complex one. CNC Drilling...

What is Machining Process? A Beginner’s Guide About Machining
Machining? Machining is a process in which a controlled material removal machine is used to remove some parts from the workpiece to shape it into the intended design. This process is a part of the manufacturing of many products based on metals, however it's possible...